Symptoms and Complications of Diabetes | Dka Diabetes | Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) | Complications of Hypoglycemia | Eye Complications | Nephropathy | Neuropathy | Cardiovascular Risk |Foot Complications | Skin Complications | Dental Health | Stroke Risk | Liver Disease | Digestive Problems | Infection Risk | Amputation | Complications of Insulin Resistance | Gestational Diabetes | High Blood Pressure | Macrovascular Complications | Types of Macrovascular Complications | Cheiroarthropathy | Complications of Diabetes Insipidus | Mental Health | Complications and Diet |
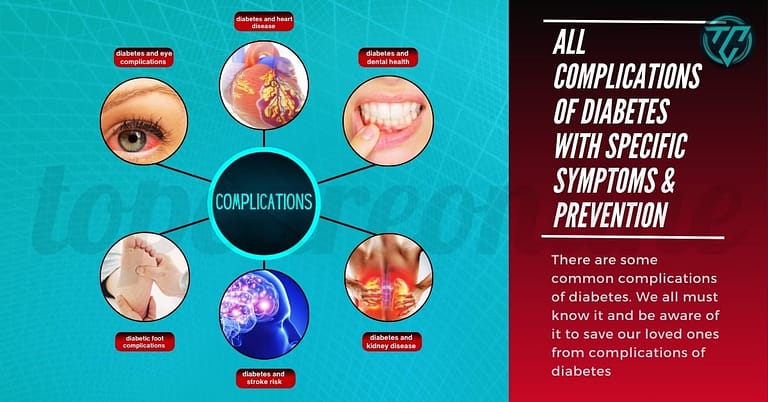
Whether it is complications of diabetes mellitus or complications of diabetes type 1 / complications of juvenile diabetes or complications of diabetes type 2, there are some common complications of diabetes.
So we all must know these complication and create diabetes complications awareness among all people. Otherwise due to complications of untreated diabetes, we will suffer a great loss.
Symptoms and Complications of Diabetes
Dka Diabetes
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a severe complication of diabetes mellitus, primarily affecting individuals with type 1 diabetes. It can lead to several serious complications if not promptly treated.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Cerebral Edema |
| Abdominal pain | Electrolyte Imbalances |
| Rapid, deep breathing (Kussmaul respirations) | Acute Kidney Injury |
| Fatigue | Cardiovascular Complications |
| Excessive thirst and frequent urination | Sepsis |
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)
Diabetic hyperosmolar coma, also known as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), is a serious complication of diabetes characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels, severe dehydration, and altered mental status, often leading to coma.
It is more common in people with type 2 diabetes, especially among the elderly and those with concomitant illness or infections. Understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment of HHS is crucial for managing and preventing this life-threatening condition.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Extremely high blood glucose levels | Hypovolemic Shock |
| Confusion, drowsiness, or coma | Renal Failure |
| Weakness or paralysis | Neurological Effects |
| Vision problems | Thromboembolic Events |
| Dry mouth and extreme thirst | Infections |
Complications of Hypoglycemia
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Sweating | Impaired Cognitive Function |
| Shakiness or tremors | Loss of Consciousness |
| Hunger | Cardiovascular Effects |
| Blurred vision | Mood and Emotional Effects |
| Palpitations or rapid heartbeat | Worsening Diabetes Control |
Diabetes and Eye Complications
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Blurred or distorted vision | Diabetic Retinopathy |
| Floaters or dark spots in the vision | Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) |
| Poor night vision | Cataracts |
| Difficulty perceiving colors | Glaucoma |
| Loss of vision in severe cases | diabetic papillopathy |
Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetes and kidney disease, is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus and one of the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. It primarily affects individuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, though the risk is higher in those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels over an extended period.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Protein in the urine (foamy urine) | Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) |
| Swelling in the feet, ankles, or hands (edema) | End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD) |
| Increased blood pressure | Cardiovascular Disease |
| Nausea and vomiting in advanced stages | Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
| Itchy skin | Anemia |
By taking right steps in the right time, definitely increase chance to lead a better life with Diabetic Nephropathy.
Diabetes and Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common and serious complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting various nerves throughout the body due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels. Neuropathy can manifest in different ways depending on the nerves affected and the severity of the condition. Thus it is crucial to know relation between diabetes and nerve damage.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Sexual dysfunction | Sensory Neuropathy |
| Bladder problems (incomplete emptying) | Autonomic Neuropathy |
| Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankle | Motor Neuropathy |
| Muscle weakness | Dry Skin |
| Sharp pains or cramps | Ulcers and Infections |
Diabetic neuropathy is a progressive condition that requires ongoing management and care to prevent complications and improve quality of life for individuals affected by diabetes.
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), which includes conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. The relationship between diabetes and cardiovascular disease is complex and multifactorial, involving several interrelated mechanisms. Like:
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Chest pain (angina) | Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) |
| Shortness of breath | Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) |
| Irregular heartbeat | Stroke |
| Swelling in the legs | Heart Failure |
| Fatigue | Arrhythmias |
By addressing these factors comprehensively, individuals with diabetes can mitigate their cardiovascular risk and improve overall health outcomes. Early intervention and ongoing management are key to reducing the impact of diabetes on cardiovascular health.
Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic foot complications are a significant concern for individuals with diabetes, particularly those who have had the disease for a long time or have poorly controlled blood sugar levels. These complications can range from minor issues such as corns and calluses to more severe problems like foot ulcers and infections.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Sores or ulcers that are slow to heal | Neuropathic Ulcers |
| Infections | Charcot Foot |
| Swelling in the foot or ankle | Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) |
| Pain in the legs | Gangrene |
| Ingrown toenails or toenail infections | Amputation |
Diabetic foot complications require proactive management and vigilance to prevent serious consequences. By incorporating good foot care habits and maintaining overall diabetes management, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing foot complications and maintain foot health.
Diabetes and Skin Complications
Diabetes can lead to various skin complications due to its effects on circulation, immune function, and the skin’s ability to heal. These skin complications can range from mild to severe and require careful management to prevent infections and other complications. Here are some symptom and Complications of common skin issues associated with diabetes:
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Skin feels dry, rough, and may appear flaky or scaly, especially on the legs, feet, and hands. | Dry Skin (Xerosis) |
| Painful red bump on the eyelid | Bacterial Infections |
| light brown, scaly patches on the skin | Diabetic dermopathy |
| raised, yellow-brown patches | Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum(NLD) |
| Thickened, tight skin on the back of the hands, fingers, or toes; may make joint movement difficult. | Digital Sclerosis |
By addressing these factors proactively and incorporating good self-care practices, individuals with diabetes can minimize the impact of skin complications and maintain healthy skin and overall well-being. Prompt medical attention is essential for any concerning changes or symptoms to prevent complications from progressing.
Diabetes and Dental Health
Diabetes can have significant implications for dental health, affecting the gums, teeth, and overall oral cavity. The relationship between diabetes and dental health is bidirectional, meaning diabetes can impact oral health, and poor oral health can complicate diabetes management.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Red, swollen gums | Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease) |
| Bleeding gums | Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) |
| Gum recession | Thrush (Candidiasis) |
| Loose teeth | Delayed Wound Healing |
| Bad breath | Increased Risk of Tooth Decay |
By prioritizing good oral hygiene, regular dental care, and effective diabetes management, individuals with diabetes can minimize the impact of diabetes on their dental health and enjoy better overall well-being.
Diabetes and Stroke Risk
Diabetes increases the risk of stroke through several interconnected mechanisms, each of which contributes to vascular damage and an elevated likelihood of experiencing a stroke. B
Connection Between Diabetes and Stroke Risk
1. Atherosclerosis:
– High blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves controlling the heart and blood vessels.
– This damage leads to the build-up of plaques (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, which can restrict or block blood flow to the brain.
2. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure):
– Diabetes often coexists with high blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for stroke.
– Hypertension puts extra strain on blood vessels, increasing the likelihood of rupture or blockage.
3. Dyslipidemia:
– Diabetes is associated with abnormal levels of lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) in the blood.
– High levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and low levels of HDL (good cholesterol) contribute to atherosclerosis.
4. Inflammation:
– Chronic inflammation in diabetes can lead to vascular damage and increased risk of stroke.
5. Obesity:
– Common in Type 2 diabetes, obesity increases the risk of stroke through various mechanisms, including increased blood pressure and dyslipidemia.
Diabetes and Liver Disease
Diabetes and liver disease can have significant complications, especially when they coexist or when one condition exacerbates the other. Here are some key complications:
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Hypoglycemia Risk
- Impaired Drug Metabolism
Diabetes and Digestive Problems
Diabetes can cause digestive problems primarily due to its effects on the nerves (neuropathy) and blood vessels (microvascular complications) throughout the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Some symptoms of Gastrointestinal Issues be like :
- Gastroparesis
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Esophageal Dysmotility
- Gallbladder Disease
Diabetes can lead to various digestive complications, primarily due to its effects on the nerves, blood vessels, and overall metabolic processes. Here are some common digestive complications associated with diabetes:
- Gastroparesis
- Diabetic Enteropathy
- Esophageal Dysfunction
- Liver Complications
- Pancreatic Dysfunction
Managing digestive problems in individuals with diabetes often involves a combination of strategies, including maintaining good blood sugar control, making dietary adjustments, managing medications carefully, and addressing specific symptoms as they arise. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers are essential to prevent and manage these complications effectively.
Diabetes and Infection Risk
Diabetes can increase the risk of infections due to several factors related to its impact on the immune system and other physiological processes.
- High Blood Glucose Levels
- Impaired Immune Response
- Poor Circulation
- Neuropathy
Complications of Gestational Diabetes
Complications for the Mother
- Pre-eclampsia
- Cesarean Delivery (C-Section)
- Increased Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
- Gestational Hypertension
Complications for the Baby
- Macrosomia (Large Baby)
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Preterm Birth
- Increased Risk of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Jaundice
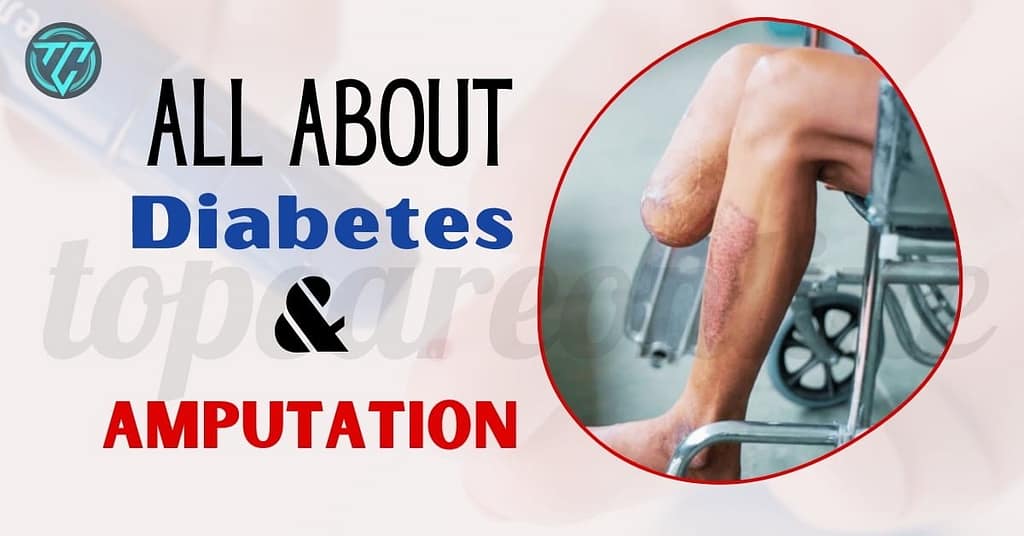
Diabetes and Amputation
Amputation is the surgical removal of all or part of a limb or extremity, such as an arm, leg, foot, hand, toe, or finger. It is typically performed to remove diseased, damaged, or infected tissue to prevent the spread of disease or to improve the patient’s quality of life. Amputations can result from a variety of causes, including severe injuries, infections, tumors, or chronic conditions like diabetes and peripheral arterial disease.
Connection Between Diabetes and Amputation
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Poor Blood Glucose Control
- Infections
Complications of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, which helps regulate blood glucose levels. When cells resist insulin’s effects, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate, leading to high insulin levels (hyperinsulinemia). Over time, this can cause various complications and is often a precursor to type 2 diabetes and other serious health conditions. Here are the major complications associated with insulin resistance:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- Cancer
- Obesity
- Sleep Apnea
Diabetes and High Blood Pressure
Diabetes and high blood pressure (hypertension) often coexist, and their combination significantly increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, kidney disease, and other complications. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and hypertension, recognizing their combined impact on health, and implementing effective management strategies are crucial for reducing the risks associated with these conditions.
Connection Between Diabetes and High Blood Pressure
Shared Risk Factors
- Obesity: Both conditions are often associated with obesity, which increases the strain on the cardiovascular system and can lead to insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet: High intake of salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to both high blood pressure and poor blood glucose control.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is a common risk factor for both diabetes and hypertension.
Pathophysiological Links
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance can lead to higher insulin levels, which may increase blood pressure by promoting sodium retention and increasing sympathetic nervous system activity.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Both diabetes and hypertension can cause damage to the endothelial cells lining the blood vessels, leading to reduced nitric oxide production and impaired vasodilation.
Compounding Effects
- Cardiovascular Strain: High blood glucose levels and high blood pressure both strain the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other vascular complications.
- Kidney Damage: Both conditions can damage the kidneys, leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and further exacerbating hypertension.
- Description: Narrowing of the arteries in the legs and feet, leading to poor circulation.
- Symptoms: Leg pain when walking, cold feet, and slow-healing sores.
Diabetes and Macrovascular Complications
Macrovascular complications are a significant concern for individuals with diabetes, as they involve damage to large blood vessels, leading to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. These complications include coronary artery disease (CAD), cerebrovascular disease (stroke), and peripheral artery disease (PAD). The presence of diabetes accelerates the process of atherosclerosis, where plaques build up on the inner walls of arteries, leading to narrowed and hardened arteries. This makes managing diabetes and its associated risk factors crucial for preventing these serious conditions.
Types of Macrovascular Complications
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Description: CAD occurs when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis.
- Symptoms: Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attacks.
- Impact: Leading cause of death in people with diabetes.
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Stroke)
- Description: Stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients.
- Symptoms: Sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, difficulty seeing, loss of balance or coordination.
- Impact: Increased risk of stroke in people with diabetes.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
- Description: PAD occurs when the arteries in the legs and feet become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the lower extremities.
- Symptoms:
- Leg pain when walking (claudication)
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot
- Sores on the toes, feet, or legs that won’t heal
- Impact: Increased risk of amputation in severe cases.
Diabetes Cheiroarthropathy
Diabetes cheiroarthropathy, also known as diabetic stiff hand syndrome or limited joint mobility syndrome, is a condition characterized by thickened skin and limited mobility of the joints, particularly in the hands. It is more commonly observed in individuals with long-standing diabetes, both type 1 and type 2. This condition can significantly affect the quality of life by impairing hand function and dexterity.
| SYMPTOMS | COMPLICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Skin Changes | Decreased Range of Motion |
| Joint Stiffness | Hand Function Impairment |
| Prayer Sign | Skin Changes |
| Functionality Impairment | Contractures |
| Glycosylation of Proteins | Pain and Discomfort |
Complications of Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) can lead to several complications if not properly managed. Here are some of the potential complications:
1. Dehydration:
The primary concern with diabetes insipidus is excessive urination, which can lead to dehydration if fluid intake does not match the output.
2. Electrolyte Imbalance:
Constant urination can cause imbalances in electrolytes such as sodium and potassium, leading to symptoms like weakness, fatigue, and in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias.
3. Fatigue and Weakness:
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can contribute to feelings of weakness and fatigue.
4. Increased Thirst:
Due to the body’s attempt to compensate for fluid loss, individuals with DI often experience excessive thirst.
Diabetes and Mental Health
Diabetes can have significant implications for mental health, affecting both emotional well-being and cognitive function. Here are some ways in which diabetes can impact mental health:
- Emotional Impact
- Diabetes Distress
- Cognitive Function
- Risk of Depression
- Anxiety
Diabetes Complications and Diet
a balanced diet for someone with diabetes should focus on:
- Complex Carbohydrates: Foods that are low in glycemic index (GI) and high in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits.
- Lean Proteins: Skinless poultry, fish, tofu, legumes, and low-fat dairy products.
- Healthy Fats: Sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil.
- Limited Saturated and Trans Fats: Found in processed foods, fried foods, and fatty meats.
- Moderate Sodium: Limiting salt intake to help manage blood pressure.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting diet and medication accordingly.
I hope through this blog you can get a crystal clear idea about all the complications of diabetes