Diabetes Feet | How Diabetes cause foot problem | Foot Symptoms | Foot Complications | Foot Treatment | Best Shoes for Diabetic Feet | How to Prevent Diabetic Foot Problems |
What is Diabetes Feet
Diabetic feet refer to the range of foot complications that can arise due to diabetes, including neuropathy, poor circulation, foot ulcers, and increased susceptibility to infections. Proper foot care and diabetes management are essential in reducing the risk of these complications and maintaining overall foot health.
How Diabetes cause foot problem
Diabetes causes foot problems primarily through neuropathy (nerve damage) and vascular (circulatory) complications. Neuropathy leads to loss of sensation and motor function in the feet, while vascular issues impair blood flow and compromise the body’s ability to heal wounds and fight infections.
1. Neuropathy (Nerve Damage):
Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a common complication of diabetes that can significantly affect the feet and lower extremities. Here’s how neuropathy contributes to diabetic foot problems and what can be done to manage and prevent them:
How Neuropathy Affects the Feet:
- Loss of Sensation
- Increased Risk of Injury
- Altered Foot
- Shape and Function
2. Vascular (Circulatory) Complications:
Vascular complications in diabetes refer to problems that arise due to damage to the blood vessels caused by chronically high blood sugar levels. These complications primarily affect the arteries that carry blood from the heart to various parts of the body, including the lower extremities (legs and feet). Here’s an overview of vascular complications in diabetes, particularly focusing on how they impact the feet:
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
- Delayed Wound Healing
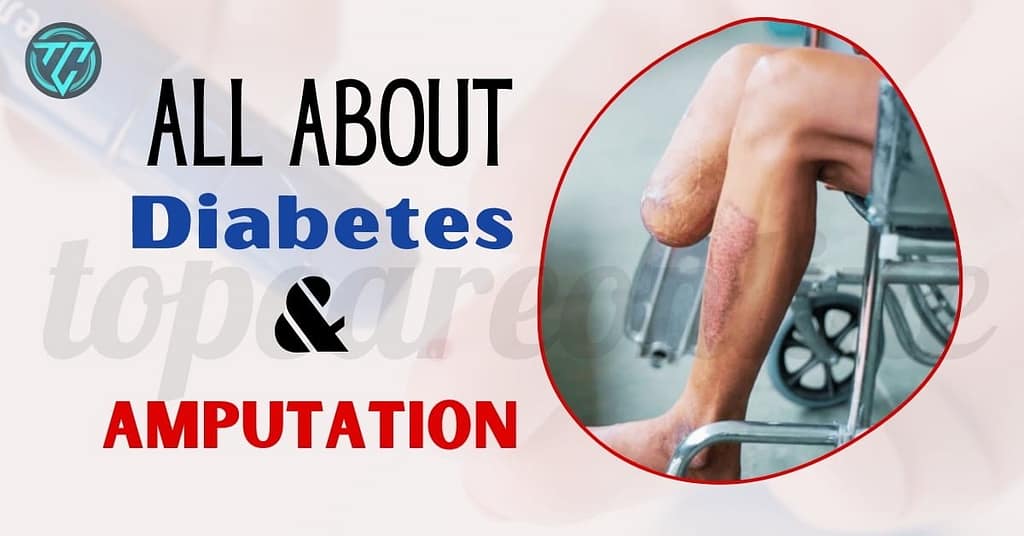
- Increased Risk of Amputation
Proper management of diabetes, including regular foot care and monitoring, is crucial in preventing or minimizing these complications and maintaining foot health.
Diabetic Foot Symptoms
Diabetic foot symptoms can vary depending on the specific complications a person experiences due to diabetes. Here are some common symptoms associated with diabetic foot problems:
- Numbness or Loss of Sensation
- Pain or Discomfort
- Changes in Skin Color or Temperature
- Slow Healing Wounds
It’s important for individuals with diabetes to regularly inspect their feet for any changes or symptoms, as early detection and prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications.
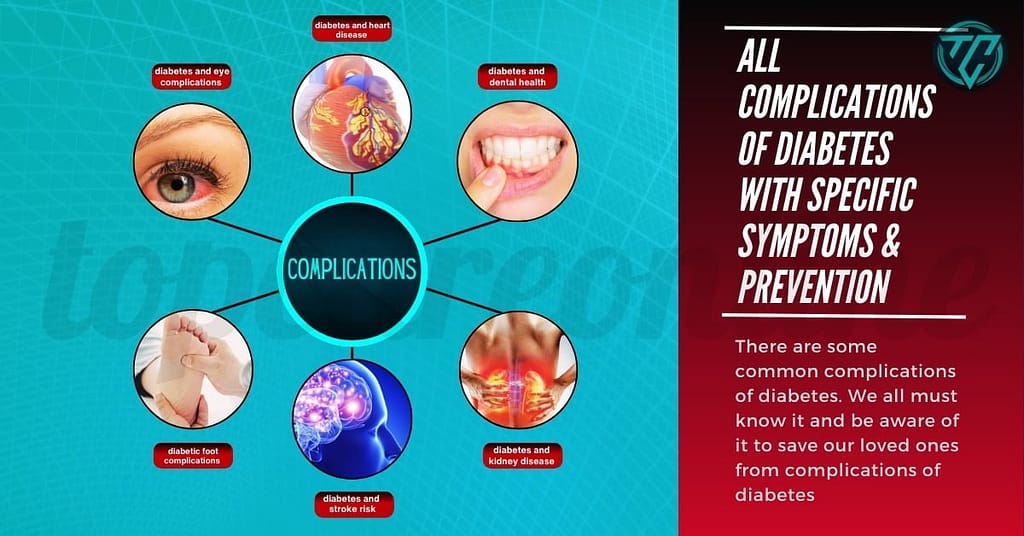
Diabetic Foot Complications
Diabetic foot complications are serious conditions that can arise due to the effects of diabetes on the nerves, blood vessels, and immune system. These complications can lead to severe consequences if not properly managed. Here are some common diabetic foot complications:
Foot Ulcers
Ulcers are open sores or wounds on the feet that are slow to heal. They typically develop due to a combination of factors including neuropathy (loss of sensation), poor circulation, and pressure from shoes or friction. Foot ulcers can become infected and, if not treated promptly, may lead to more severe complications such as gangrene.
Infections
Due to impaired circulation and compromised immune function, individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections in their feet. Infections can occur in ulcers, cuts, or even in the bones (osteomyelitis), and they can spread rapidly if not treated promptly. Diabetic foot infections can be challenging to treat and may require antibiotics or even surgical intervention.
Charcot Foot
Charcot foot is a condition where the bones in the foot weaken and fracture, often occurring in individuals with neuropathy. The loss of sensation prevents the person from feeling pain, leading to continued walking on the injured foot and further damage. Charcot foot can cause significant deformity and instability of the foot.
Amputation
In severe cases of diabetic foot complications, where ulcers, infections, or gangrene cannot be controlled or treated effectively, amputation of part of the foot or leg may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection and save the person’s life.
Early intervention and preventive measures are crucial in reducing the risk of diabetic foot complications and maintaining foot health.
Diabetes Foot Treatment
The treatment of diabetes-related foot problems depends on the specific issue or complication present. Here are key treatments for common diabetes foot conditions:
1. Foot Ulcers
Wound Care:
Proper wound care is essential. This involves cleaning the ulcer with mild soap and water, applying an antibiotic ointment if necessary, and covering it with a sterile dressing.
Offloading:
Offloading pressure from the ulcerated area is crucial to promote healing. This can be achieved through special shoes, casts, removable walking boots, or custom orthotic devices.
Infection Control:
If the ulcer becomes infected, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection effectively.
2. Charcot Foot
Immobilization:
The affected foot may need to be immobilized with a cast or special footwear to prevent further damage and promote healing.
Offloading:
Offloading pressure from the affected area is crucial to prevent complications and promote stability.
3. Infections
Antibiotics:
Depending on the severity and type of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed orally or intravenously to treat bacterial infections.
Wound Care:
Proper wound care techniques, including cleaning, debridement if necessary, and dressing changes, are essential to promote healing and prevent further infection.
It’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to actively participate in their foot care and work closely with their healthcare team to prevent complications and maintain optimal foot health. Early intervention and consistent management are key to reducing the risk of serious foot problems and improving overall quality of life.
Best Shoes for Diabetic Feet
Choosing the best shoes for diabetic feet is crucial to prevent foot complications and promote comfort and safety. Here are some key features to look for when selecting shoes for individuals with diabetes:
- Comfort and Fit
- Support and Cushioning
- Breathability
Tips for Shoe Selection:
- Get Professionally Fitted:
- Visit a specialized footwear store or podiatrist to get professionally fitted for shoes that meet your specific needs.
- Check for Approval:
- Look for shoes that are approved by the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA) or recommended by healthcare professionals specializing in diabetic foot care.
Choosing the right shoes is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications such as foot ulcers, infections, and injuries. It’s essential to prioritize comfort, fit, support, and safety when selecting footwear to maintain optimal foot health.
How to Prevent Diabetic Foot Problems
Preventing diabetic foot problems is crucial for maintaining overall foot health and avoiding serious complications. Here are some key steps and strategies to help prevent diabetic foot problems:
1. Daily Foot Care Routine:
Inspect Your Feet Daily: Check your feet thoroughly every day, including between the toes and the soles, for any cuts, sores, blisters, redness, swelling, or changes in skin color or temperature.
Clean Your Feet Properly: Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Avoid soaking your feet, as it can dry out the skin excessively. Gently pat your feet dry, especially between the toes.
Trim Nails Carefully: Trim your toenails straight across and smooth the edges with a nail file. Avoid cutting into the corners or cutting the nails too short, as this can lead to ingrown toenails.
2. Proper Footwear and Foot Protection:
3. Quit Smoking and Manage Other Health Conditions:
Preventing diabetic foot problems requires a proactive approach to foot care, including daily inspection and care, proper management of blood sugar levels, wearing appropriate footwear, regular foot exams, and addressing foot issues promptly.
By implementing these preventive strategies and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of foot complications and maintain optimal foot health.