Can Weight Loss Be Caused by Diabetes? | Why do Diabetics Lose Weight | Lose Weight in Their Legs | Increases the Risk of Amputation | Managing Weight Loss
If you or someone you know has diabetes, you might have noticed some concerning changes in body weight, particularly in the legs. It’s a question that often arises: why do diabetics lose weight in their legs?
This blog post will delve into the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, exploring why diabetes can lead to weight loss, especially in the legs, and how you can manage or mitigate these effects.
Can Weight Loss Be Caused by Diabetes?
Yes, weight loss can be a direct result of diabetes. Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can lead to weight loss, though the mechanisms differ:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This form involves the autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to severe insulin deficiency. The body starts breaking down fat and muscle tissues to meet its energy needs, resulting in weight loss.
- Type 2 Diabetes: While Type 2 diabetes often starts with insulin resistance, prolonged high blood sugar and poor glucose control can also lead to weight loss through similar mechanisms of muscle and fat breakdown.
Why do Diabetics Lose Weight
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). When diabetes is not well-managed, it can lead to various complications, including unintended weight loss.
Get to Know a Broad Idea About
This weight loss often affects specific parts of the body, such as the legs. You might have noticed that your legs are becoming skinny or losing muscle mass , you’re not alone. Here’s why do diabetics legs get skinny:
- Insulin Resistance and Muscle Loss: In people with diabetes, especially Type 2, insulin resistance is a key issue. Insulin is essential for nutrient absorption and energy storage. When cells become resistant to insulin, glucose cannot enter cells efficiently, leading to muscle breakdown as the body tries to find alternative energy sources. This muscle loss can be more noticeable in the legs due to their significant muscle mass.
- Poor Blood Circulation: Diabetes can impair blood circulation, especially in the extremities. Poor circulation reduces the delivery of nutrients to muscle tissues in the legs, which can contribute to muscle wasting and weight loss.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: This condition involves nerve damage caused by high blood sugar levels. It can lead to weakness and atrophy of the muscles in the legs, further contributing to weight loss in this area.
- Increased Catabolism: Diabetes can alter the body’s metabolism, leading to increased breakdown of fat and muscle tissues for energy. This heightened catabolic state can disproportionately affect the legs.
- Inadequate Nutrition: Sometimes, diabetes management plans may inadvertently lead to inadequate nutrition. If a diabetic person’s diet is not well-balanced, it might lack sufficient protein and essential nutrients needed for muscle maintenance, exacerbating weight loss in the legs.
Why do Diabetics Lose Weight in Their Legs?
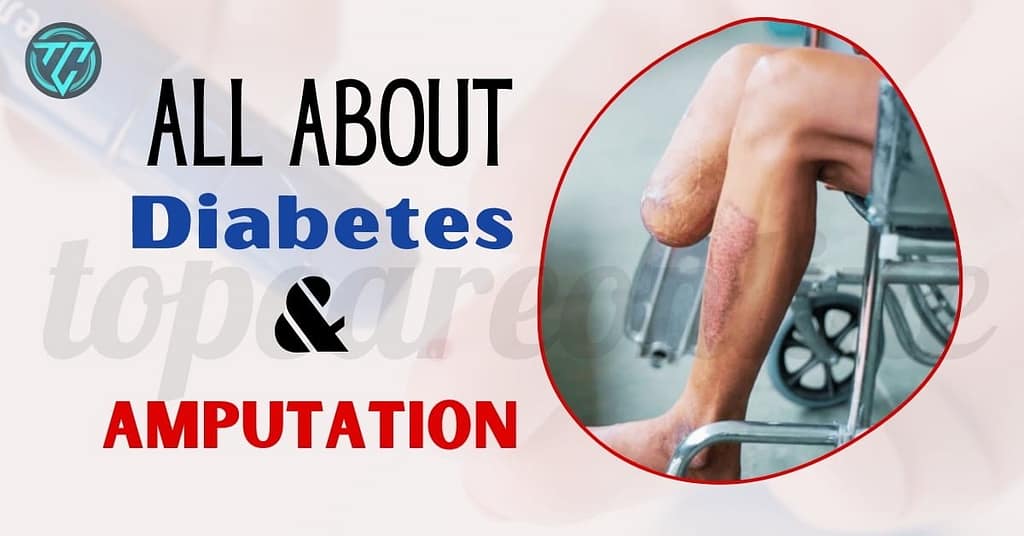
A related and more severe concern is the loss of limbs, which can occur due to complications of diabetes, such as diabetic foot ulcers and infections.
Read Out the relation between Diabetes and Feet Through
High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, making the legs and feet more susceptible to severe conditions. Here’s how we can get an answer for why do diabetics lose limbs:
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Prolonged high blood sugar can lead to foot ulcers that are difficult to heal. If these ulcers become severe, they can lead to infections and, in extreme cases, require amputation.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Diabetes increases the risk of PAD, a condition where arteries in the legs are narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow and leading to severe complications.
- Gangrene: Infected and poorly healing wounds can lead to gangrene, a serious condition where body tissues die. This often necessitates limb amputation to prevent the spread of infection.
How Diabetes Increases the Risk of Amputation
Diabetes, particularly when poorly managed, can lead to serious complications, one of the most severe being amputation. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and amputation is crucial for prevention and effective management.
Have a close look at why does diabetes cause foot loss
Here’s a detailed look at how diabetes can increase the risk of amputation and the steps to mitigate these risks.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): In PAD, reduced blood flow to the extremities can lead to severe pain, ulcers, and wounds that are slow to heal. If untreated, this can result in tissue death (gangrene) and the need for amputation.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: It primarily affects the feet and legs, leading to:
- Loss of Sensation: Reduced or lost sensation in the feet can result in unnoticed injuries, cuts, or blisters. These minor injuries can become serious if they are not detected and treated promptly.
- Increased Risk of Ulcers: Nerve damage can also impair the body’s ability to detect and respond to foot injuries, increasing the risk of diabetic foot ulcers.
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: These are open sores that develop on the feet, often due to pressure or trauma combined with poor circulation. Key factors include:
- Infection: Foot ulcers can easily become infected. Diabetes can impair the immune system and reduce the body’s ability to fight infections, making healing difficult.
- Gangrene: If an infection progresses, it can lead to gangrene (tissue death), which may necessitate amputation to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Poor Blood Sugar Control: Consistently high blood sugar levels exacerbate all the above complications by:
- Accelerating Damage: High blood sugar accelerates damage to blood vessels and nerves, worsening PAD and neuropathy.
- Impeding Healing: Elevated glucose levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, making infections and ulcers more severe and harder to manage.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Diabetes can compromise the body’s immune response, making infections more likely and harder to treat. In severe cases, infections that develop in the legs or feet can lead to amputation if they are not controlled effectively.
That’s why, why do diabetes lose limbs and bear a lifetime pain.
Managing Weight Loss in Diabetics
Managing weight loss, especially in the legs, involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Optimize Blood Sugar Control: Effective diabetes management through diet, medication, and regular monitoring can help prevent the complications that lead to muscle loss and weight loss.
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure a diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to support muscle maintenance and overall health. Consulting with a dietitian can help create a tailored plan.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in strength-training exercises to build and maintain muscle mass. Activities such as resistance training and leg exercises can help counteract muscle loss.
- Monitor Foot Health: Regularly check for any foot injuries or ulcers. Good foot care practices, including proper footwear and hygiene, can prevent severe complications.
- Consult Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help manage and address any issues related to diabetes and weight loss effectively.
If you have concerns about weight loss or other diabetes-related issues, don’t hesitate to seek advice from healthcare professionals. Together, you can work towards a healthier and more balanced life.